How Many Different Sums Of Money Can Be Made From A Penny A Nickel A Dime And A Quarter
Curriculum for Form i
Students wait nether the hood of add-on and subtraction, applying place value understanding to 2-digit operations.
MODULE ane. Sums and Differences to 10
Topic A: Embedded Numbers and Decompositions
Students learn addition to 5 using concrete objects, abstract objects and equations. They learn the meaning and proper use of + and = signs, also equally the terms "addend" and "sum."
Topic B: Counting On from Embedded Numbers
Students acquire add-on to 10 using concrete objects, abstract objects, equations and number bonds. They solve for missing addend problems and begin to represent and solve discussion problems.
Add 0 to a number
Students add together zero to a single-digit number. They solve equations in which cypher is the starting time addend and when it is the second addend

Use the + sign in an equation and find the sum
Students add single-digit numbers equally represented by colored cubes. They choose the + sign to complete an equation and decide the sum

Model and solve an addition equation
Students apply colored cubes to represent the addends in an equation and so make up one's mind the sum

Record an improver equation based on a model to bear witness more one mode to attain a given sum
Students write an addition equation to match a given model of cubes. They repeat this skill with some other equation with the same sum and observe that there is more one way to show that sum

Show more than one way to achieve a given sum
Students write an addition equation to match a given model of cubes. Then they create another cube model with the same sum and record the equation, observing that there is more than i way to bear witness that sum

Solve an addition equation (totals to vii)
Students determine the sum for addition equations with two addends and totals to 7

Identify parts of an addition equation
Given an addition equation, students place the showtime addend, 2d addend, plus sign and sum

Record an add-on equation based on a model and create a model to show more than than one way to reach a given sum
Students write an addition equation to match a given model of cubes. Then they create another cube model with the aforementioned sum and record the equation, observing that there is more than 1 mode to show that sum

Solve addition equations to x with or without a model
Students choose whether or not to view a cube model in order to solve add-on equations to 10 then solve

Solve an addition equation (totals to ten)
Students determine the sum for addition equations with two addends and totals to 10

Model and solve an addition word problem with objects
Students write and solve an improver equation based on colored objects. They then utilise objects as directed to model an improver scenario, write it as an equation, and solve for the total period

Model and solve an addition word trouble with cubes
Students use cubes to model an add-on scenario, write it every bit an equation, and solve for the total

Write and solve an addition equation based on a word problem
Students write an equation based on an improver scenario and solve it

Determine the missing addend based on a model of cubes
Students determine the missing second addend in an equation based on colored cubes. Starting time, hints direct them to the role of the model to detect the answer. Then, students solve without the hint

Make up one's mind the missing addend in an equation (Part 1)
Students make up one's mind the missing 2nd addend in an equation

Determine the missing addend in an equation (Role ii)
Students make up one's mind the missing second addend in an equation, choosing whether to solve immediately or model with cubes. Then they decide the missing start or second addend in an equation

Determine the missing addend in a number bond
Students determine the missing second addend in an equation. Then they make up one's mind the missing addend in a number bond for multiple number bonds with the aforementioned total

Choose ii addends to reach a given total
Students determine the missing second addend in an equation, choosing whether to solve immediately or model with cubes. They identify which of ii equations is true. Students and then choose two addends to accomplish a given total

Solve missing addend add-on equations
Students make up one's mind the missing second addend in an equation

Identify addends with a sum of x
Students identify which of two add-on sentences with sums to 10 is right. They identify pairs of addends that take a sum of ten

Identify a number bond
Students determine the total number of objects then its two addends based on colour. They drag these values into a number bond. Students then identify a number bond amidst three images

Build a number bond based on a model of cubes
Students build a number bond based on a model of colored cubes and then write information technology as an improver equation. Then, students write the equation first, based on the model of cubes, and build the number bail

Build a number bond based on a model of cubes and consummate its addition equation
Based on a model of colored cubes, students complete the missing addend in a number bond and its related add-on equation. And so, they complete the entire number bail based on a model of cubes

Build a model, number bond, and equation
Students create a two-color model of circles. They build a number bond based on the model and determine a missing addend or sum in its related equation

Consummate a number bond
Students determine the missing addend in a number bail. Then, they determine ii addends that consummate a number bail with a given total

Consummate a number bond to show more than 1 mode to reach a given total
Students determine 2 addends that complete a number bail with a given total. Then, they determine two different addends to complete a number bond with that aforementioned full

Topic C: Development of Addition Fluency Within x
Students reinforce their understanding of addition within 10 and its underlying concepts as they build more efficient strategies to solve problems. They use improver scenarios with objects, base-ten block patterns, the number line, and equations to reinforce the relationships amid fact families. They build upon existing knowledge of composition of numbers 6-10 as they motion from the concrete to the abstract.
Identify a missing addend in equations with a sum and their turnaround facts
Summate a missing addend in equations that sum to a maximum value of 10 with visual support. Also calculate a missing addend in equations that sum to maximum value of ten using turnaround facts, or switching addends that sum to a maximum value of 10

Record a model of base of operations-ten blocks as an addition equation
Use base of operations 10 blocks and/or turnaround facts to complete an addition equation. These equations will sum to 10 each fourth dimension

Identify the missing addend in equations paired as turnaround facts with sums of iv, 5, 6 and 7
Identify a missing addend in equations that sum to 4,5,6, or 7. Students volition also use turnaround facts to place mssing addends

Solve for a missing addend in an equation
Solve for a missing addend in an equation. Students will use an interactive game to assistance guide them through solving for the missing addends

Identify the missing addend in equations paired as turnaround facts with sums of 6, 7, 8 and 9
Identify a missing addend in equations that sum to vi,7,8, or ix. Students will too utilize turnaround facts to place mssing addends

Choose the correct sum for an addition expression
Choose from a selection of 2 answers for each numerical expression they are given. Each numerical expression sums to ane of the two answers

Identify the missing addend in equations paired as turnaround facts with sums of nine and 10
Place a missing addend in equations that sum to 9 or x. Students will also use turnaround facts to identify mssing addends

Topic D: Decomposition Strategies for Subtraction
Students reinforce thier understanding of subtraction within ten and its underlying concepts as they build more efficient strategies to solve problems. They explore the human relationship betwixt improver and subtraction and piece of work increasingly with 0 every bit a subtrahend and departure. They utilise subtraction scenarios with objects, base-10 cake patterns, the number line, and equations to reinforce the relationships among fact families. They build upon existing noesis of composition of numbers 6-10 as they move from the concrete to the abstract.
Record a scenario based on objects as a subtraction equation with a difference of 0 (Part ii)
Write subtraction equations using two numbers. They volition write these subtraction equations to match with a flick they are given

Tape a number line scenario as a -0 subtraction equation
Learn that subtracting 0 from a number gives you the number you lot started with using a number line. Students will have to identify both numbers being subtracted and the difference based on the number line scenario

Record a number line scenario as a subtraction equation with a difference of 0
Learn that subtracting a number from itself results in a departure of 0 using a number line. They will identify the difference after beingness prompted to interact with the number line

Place missing numbers in subtraction equations with a difference of 0
Solve for missing elements in subtraction equations that outcome in a difference of 0. Identify either one of the numbers that result in a difference of 0 or the deviation of 0 iteself depending on the case

Subtract past moving an object astern on a number line and solve a related equation that shows subtraction from 3, 4, or 5
Subtract numbers from 3,4, or 5 using a number line. Sometimes, students will be prompted to fill in one missing chemical element in a subtraction equation after interacting with the number line scenarios

Tape a number line scenario every bit an equation that shows subtraction from 3, iv, or v
Subtract numbers from 3,4, or 5 using a number line. Students will exist prompted to fill in all elements of a subtraction equations including the minuend, operations symbol, subtrahend, and difference

Record a scenario based on objects as a subtraction equation with a divergence of 0 (Part i)
Use a scenario illustrated with pictures to complete subtraction equations. Students volition make full in the minuend, subtrahend, and difference for each subtraction equation

Use base-ten blocks to represent subtraction scenarios with objects within 5 and place base-10 block patterns that represent subtraction scenarios with objects inside 5
Select the number of base 10 cubes that match the number of objects removed in the scenario illustrated with pictures. They difference left over should match the number of pictures left over

Solve equations based on a model of base-10 blocks to subtract ane or all simply i
Click the number of base 10 cubes that should be taken away from the total to match the difference of the subtraction equation given to yous. Afterwards, students volition in the difference of the subtraction equation

Record a model of base-10 blocks as 2 related equations that prove subtraction from half dozen
Make full in addends and sums in equations that add up to vi given a scneario illustrated by base of operations x cubes. Students will then consummate two subtraction equations using 6 and the addends from the showtime equation

Tape a model of base of operations-ten blocks equally two related equations that show subtraction from 7 or 8
Fill in addends and sums in equations that add upwardly to 7 or 8 given a scneario illustrated by base x cubes. Students will then complete two subtraction equations using 7 or viii and the addends from the kickoff equation

Subtract by moving an object backward on a number line and solve a related equation that shows subtraction within seven
Subtract numbers from vii using a number line. Students will then exist prompted to fill in the difference of subtraction equations

Tape a number line scenario as an equation that shows subtraction from vii
Fill in all elements of an addition equation that sums to vii including the addends, operation symbol, and sum using a number line scenario. Students will be prompted to complete a subtraction equation starting with 7 and the subtracting smaller numbers

Record a model of base of operations-10 blocks as two related equations that prove subtraction from 9 or 10
Fill up in addends and sums in equations that add up to 9 or 10. given a scneario illustrated by base 10 cubes. Students will then complete ii subtraction equations using ix or 10 and the addends from the offset equation

Solve addition and subtraction equations based on a number line model
Consummate addition and subtraction equations using a number line model. Students will only fill in either the sume of difference in the equations depending on whether the equations are addition of subtraction equations

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 9
Using base 10 cubes, fill in the missing addend and sum for addition equations that sum to nine. Too, employ base 10 cubes to make full in missing subtrahend and difference in subtraction equations that start with a minuend of 9

Topic E: Development of Subtraction Fluency Within 10
Students reinforce the relationship between addition and subtraction and the relationships among fact families. They use familiar objects, base of operations-ten blocks, the number line, and equations to explore the composition of numbers iii-ten. They build speed and accurateness with all +/- facts within 10.
Place a number line model that represents a subtraction scenario given in words
Expect at the three possible number line scenarios given to yous. Then, select the one that represents the subtraction equation written in words

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 4, 5, and 6
Using scenarios illustrated past base of operations x cubes, fill in missing elements of subtraction equations. Each of the subtraction equations volition commencement with either iv, 5, or vi

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 6 and 7
Using scenarios illustrated by base of operations ten cubes, fill in missing elements of subtraction equations. Each of the subtraction equations will starting time with either 6 or 7

Cull matching subtraction expression and departure
Using scenarios illustrated by pictures, match subtraction expressions with their corresponding differences. The activity ends when you become from one of the of the game lath to the other

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 7 and 8
Using scenarios illustrated by base of operations 10 cubes, fill in missing elements of subtraction equations. Each of the subtraction equations will offset with either seven or 8

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from eight and 9
Using scenarios illustrated by base x cubes, fill up in missing elements of subtraction equations. Each of the subtraction equations volition get-go with either 8 or 9
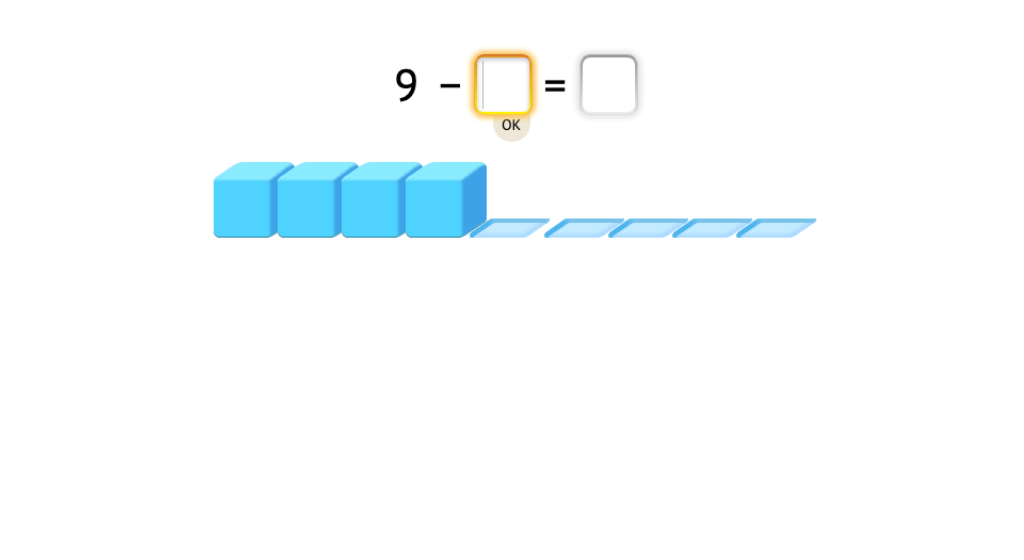
Determine the missing chemical element in a subtraction equation
Determine what elements are missing in the subtraction equations. As you fill in the missing elements of the subtraction equations, a puzzle will slowly exist completed

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from nine and 10
Using scenarios illustrated past base x cubes, fill in missing elements of subtraction equations. Each of the subtraction equations volition beginning with either 9 or 10

MODULE two. Introduction to Place Value Through Add-on and Subtraction Within twenty
Topic A: Counting On or Making Ten to Solve Result Unknown and Total Unknown Problems
Students reinforce their understanding of "tens" and "ones" while sorting, counting, adding, and subtracting. They utilize objects, base of operations-10 blocks, the number line, and a ten-frame. They do various strategies to add together across ten and increase fluency with +/- facts within 20.
Grouping base-ten rods and cubes into a ten and ones and determine totals
Using 10 cube long rods and single base ten cubes, group the rods and cubes into the tens and ones places respectively. So point how many "tens" and "ones" there are

Determine the number of tens and ones using objects or base-10 blocks grouped into a ten-frame or a rod
Starting with a certain number of objects, identify x objects into the given box. Subsequently ten objects have been placed in the box, indicate how many objects are left over

Determine the number of tens and ones using objects or base-10 blocks grouped into a ten-frame or a rod and then determine the total
Starting with a box or group of 10 objects and a group of less than 10 objects, signal how many objects are in the box and in the separate group. Then, bespeak how many objects there are overall

Determine the total number of objects or base-ten blocks grouped into a ten and ones
This activity starts with a certain number of objects grouped into tens and ones places. You must signal how many "tens" there are followed past the number of "ones." And so, point how many objects there are birthday

Determine the total number of objects past filling a ten-frame
Starting time with finishing filling upwardly a 10 slot box with objects. Later that is done, indicate how many objects there by adding up the number of objects in the box with the number of objects left outside of the box

Represent numbers in the 2nd 10 using a rod and cubes
Starting with several ten cube rods and several single cubes, elevate the number of cubes indicated in the question. Be sure to elevate the 10 cube rods to indicate 10 cubes. Don't try to elevate single cubes to indicate 10 cubes

Decide missing numbers in the 2nd ten on a number line and place their written name
This activity begins with a number line that starts with the numer ten. You will then identify each whole number after 10 by its written name

Position numbers to xix on a number line
Given each number 1 at a fourth dimension, y'all will place whole numbers that are greater than 10 and less than 20 on a number line. You will do this 1 number at a time

Determine the ii-digit total of aligned objects
Given a number of objects that are grouped in straight rows, bespeak how many objects there are. The number of objects will be greater than 10 and less than twenty

Add together to or decrease from numbers 11-20 with and without a number line model
This activeness volition be completed both with and without a number line. You will add to and subtract from numbers eleven-20

Solve +/- equations that include the number x
This activity volition be completed both with and without the utilise of base 10 cubes every bit a guide. You will complete improver equations that include the number 10 in them

Complete a series of related equations to add across ten based on a model of base-10 blocks
Base 10 blocks will exist used equally a guide for this activity. You volition complete improver equations based on the number of base 10 blocks there are in each case. Several of the sums will result in numbers greater than 10 but less than 20

Solve improver equations beyond 10 using a number line
This activity volition completed with the aid of a number line. You will complete addition equations that sum to amounts greater than 10

Add three addends by first matching ii addends to make a ten based on a visual model
Using pictures to help in grouping a given number of objects, you volition place 10 of the objects into the container. Afterward this is complete, you will determine how many objects are left and sum up the 10 previously grouped objects and the ones left over

Add three addends by first matching 2 addends to make a 10 based on a model of base-10 blocks (Part 1)
You will employ stacked base x number cubes as a guide for this activeness. Starting with 3 addends, you volition combine two of them to add to 10. Then add the the remaining amount of cubes to the x to get a final sum

Add 3 addends by commencement matching ii addends to make a ten based on a model of base-10 blocks (Function 2)
Starting with three addends, y'all will determine which two of them to add together to 10. Then add the the remaining amount of cubes to the 10 to get a final sum

Model and solve addition equations beyond 10 using base-10 blocks by making a 10
Starting with two numbers whose amounts are indicated by preset stacks of number cubes, you will sort 10 of them into a stack. So, stack the remaining cubes in a split up stack. Finally, sum up all the cubes in an improver equation

Solve +nine equations with and without a model of base of operations-10 blocks
With and without a base 10 number cube model, solve addition equations that add 9 to diverse single digit numbers. Showtime with determining which two numbers add to 10, then add together the remaining corporeality to get a sum greater than x

Solve equations with ix across ten using a number line
Using a number line and starting with the number nine, you lot will add 1 to 9 to get ten. After that, y'all will add together whatever corporeality remains to get the final sum that volition be greater than 10

Add together to numbers eleven-xx across ten
Starting with the number nine, you volition add 1 to 9 to get 10. After that, you will add whatever amount remains to go the final sum that volition be greater than 10 but less than 20

Solve +eight equations with and without a model of base-ten blocks
Using a base 10 number cube mode, y'all will outset with the number 8, you lot will add together 2 to 8 to get 10. Later on that, yous will add together whatever amount remains to get the final sum that will be greater than 10. You lot accomplish this using a base of operations 10 number cube model

Solve +viii equations with and without a model of base of operations-10 blocks
Without using a base 10 number cube model, you volition get-go with the number 8, yous will add 2 to 8 to become 10. Later on that, you will add together whatever amount remains to go the concluding sum that will be greater than 10

Solve equations with 8 across 10 using a number line
Using a number line and starting with the number 8, yous will add together ii to 8 to become 10. Afterward that, you volition add whatever amount remains to become the final sum that will be greater than ten

Solve +half-dozen and +7 equations with and without a model of base-x blocks
Using a base 10 number cube model, you will start with either the number 6 or 7, you will then add together enough cubes to 6 or 7 to get 10. Afterward that, you will add whatever amount remains to get the final sum that volition be greater than 10

Identify addends to reach a given sum of 11, 12, or 13
Given a group a numbers, you will place which pairs add together to eleven. Y'all volition then do the aforementioned for pairs that add together to 12 and 13

Solve add-on equations beyond 10 using a number line
Using a number line and starting with a number less than x, you lot volition figure out how much to add to the inital number to get to x. After that, you will add whatsoever corporeality remains to get the final sum that will exist greater than 10

Dissever an addend to make a 10 and solve an addition equation
Without using a number line and starting with a number less than 10, yous will figure out how much to add to the inital number to become to 10. Afterward that, you will add whatever amount remains to go the final sum that will exist greater than 10

Split an addend to brand a 10 based on a model of base of operations-ten blocks and solve an addition equation
Using a base 10 number cube model, place 2 separate stacks of cubes into tens and ones column. Then, determine how many cubes from the smaller stack yous demand to add to the larger one to get 10. Any remains in the smaller stack add to the equation

Identify addends to attain a given sum of 14, 15, or 16
Given a group a numbers, you lot will place which pairs add to 14. You will then practice the same for pairs that add to fifteen and xvi

Place addends to accomplish a given sum of 17, xviii, or 19
Given a group a numbers, yous will identify which pairs add to 17. You volition then do the same for pairs that add to 18 and nineteen

Solve addition equations across ten (Level 1)
Without the use of a base of operations 10 number model or a number line, you will sum together two addends to go a final sum. These terminal sums will all be greater than 10 but less than twenty

Solve add-on equations beyond ten (Level 2)
Using an interactice illustration of planets, you will complete addition equations. Each sum yous get will be greater than 10 and merely less than 20

Topic B: Counting On or Taking from Ten to Solve Result Unknown and Full Unknown Problems
Students acquire strategies for adding and subtracting beyond ten. They employ familiar models of base-10 blocks, the number line, and ten frames to illustrate the significant behind the operations.
Complete a serial of related equations to subtract across 10 based on a model of base-x blocks
Using a base 10 number cube model, you will start with a value greater than 10. Y'all will so subtract i, ii, 3, and 4 from that initial number

Solve subtraction equations beyond 10 using a number line
Using a number line and starting with a number greater than 10, you will complete subtraction equations. Yous volition more than probable get a difference less than x each time

Model and solve subtraction equations across 10 using objects in a ten-frame
Given a box or container of x objects with boosted objects outside of the box or container, you will consummate subtractio equations. you volition start with a total number of objets greater than ten each time

Model and solve subtraction equations across 10 using base-x blocks (Part 1)
Using a base 10 number cube model, complete subtraction equations. Kickoff with greater than x cubes each time that area sorted into tens and ones column. And then, remove the number cubes equivalent to the number you are subtracting from the larger number

Model and solve subtraction equations across x using base of operations-x blocks (Part 2)
Using a base 10 number cube model, complete subtraction equations. Starting time with greater than x cubes each time that area sorted into a tens and ones column. And then, remove the number cubes equivalent to the number yous are subtracting from the larger number

Solve subtraction equations within xx
Use a base ten number model. The initial number of cubes will be equivalent to the minuend. Ten of the cubes will exist placed in a tens column, the rest of the cubes in a ones column. Determine how many more cubes you demand to remove from the tens column to e

Solve subtraction equations across 10
Without the employ of any visual aids, you will complete subtraction equations. Each fourth dimension the equation starts with a number greater than 10

Solve two-digit minus 1-digit subtraction equations across 10
Using interactive illustrations, students will complete subtraction equations. These subtraction equations will all be ii digit numbers minus ane digit numbers

Topic C: Varied Problems with Decompositions of Teen Numbers as one Ten and Some Ones
Students explore place value as they add and decrease beyond 10. They use multiple representations (objects, ten-frame, number line, base-10 blocks, and equations) to move from the concrete to the abstract. Students build their fluency with +/- facts within past reinforcing the underlying concept of exchanging and using the strategy of "resting" on ten. They likewise solve +/- bug in which all ones or all tens are added or subtracted.
Solve substraction equations that include the number 10
Using a base 10 number cube model, students will complete addition and subtraction equations. Before completing each equation cubes will be added and subtracted on screen

Record a model of objects or base-x blocks as an equation that adds or subtracts all tens or all ones
Using a group of objects arranged in direct rows, a sure number of will disappear. Yous then needs to make full in all elements of the subtraction equation including the minuend, functioning symbol, the subtrahend, and the departure

Consummate equations that add together or decrease all tens or all ones with and without a model of base-10 blocks
With and without the use of base 10 number cubes, you volition complete both improver and subtraction equations. When the base of operations 10 number cubes are used, they volition either exist added or subtracted from the total before completing the subtraction equations

Add together ones to numbers in the second 10 using base-10 blocks
Using base x number cubes that are arranged in tens and ones columns to reverberate the outset addend, you will add together number cubes to the ones cavalcade equal to the second addend. After y'all add the number cubes, you then identify the final sum

Decrease from numbers 11-twenty using base-10 blocks
Using base ten number cubes that are arranged in tens and ones columns to reflect the get-go addend, y'all will remove cubes from the ones column equal to the subtrahend. After y'all remove the number cubes, you and so identify the final departure

Solve +/- equations that utilize numbers in the 2nd 10 and a single-digit number (Role 1)
You will calculate the divergence of subtraction equations in this activity. Each equation involves subtraction unmarried digit numbers from two digit numbers

Identify a missing addend to reach a sum of 20 with and without a model of base of operations-ten blocks
Using a base 10 number cube model, you determine how many cubes to add together to equal twenty number cubes. You volition then complete the corresponding addition equation

Solve +/- equations that use numbers in the 2nd ten and a unmarried-digit number (Function two)
You lot will solve add-on and subtraction equations in this activity involving a two digit number less than 20 and a single digit number. An animated illustration will progress after each each equation is answered correctly

MODULE 3. Ordering and Comparison Length Measurements as Numbers
Topic A: Indirect Comparison in Length Measurement
Students utilise familiar, real objects to build their sense of length comparing. They decide the longest, shortest, longer, and shorter among objects, even when not aligned.
Topic B: Non-Standard Length Units
Students utilize paper clips as a non-standard unit of measurement of length to measure objects. They acquire that units must measure from endpoint to endpoint with no gaps or overlaps.
Topic C: Data Interpretation
Students count real objects and employ tally marks or bar graphs to represent them. They interpret data presented in tables and graphs, and use it to find total, how many more than, and how many fewer.
MODULE iv. Identify Value, Comparison, Addition and Subtraction to 40
Topic A: Tens and Ones
Students further explore the concept that a ii-digit number is composed of a round number (tens) plus ones. They decide totals, decompose numbers, add, and decrease. Students use familiar objects, base-x blocks, 10-frames, equations, and number names forth with identify value cards. Note that the "coins" used are to reinforce the concept of tens, fives, and ones, not coin recognition.
Add tens to 40 based on a model of base-10 blocks
Given rods of 10 base ten cubes, yous will count the number of cubes by tens. During part of this activity, yous will beginning identify the number of tens and and then bespeak how many cubes at that place are in total with a maximum full of forty cubes

Determine totals to xc past counting base-ten rods
Given rods of 10 base 10 cubes, y'all will count the number of cubes by tens. During function of this activity, you will first identify the number of tens and then betoken how many cubes there are in full with a maximum total of ninety cubes

Determine totals by counting objects with or without filling 10-frames
In this activity, you lot will determine the total amound of objects shown by filling ten-frames. By ten-frame, I mean a box with a maximum capacity of x objects

Identify 2-digit round numbers
This activity deals with the mathematical thought of round numbers or numbers that end in zero. Given a group of numbers, you will identify which numbers would be considered circular

Determine totals to 40 by counting tens and ones using base-10 blocks
Base x number cubes sorted into rods of ten and remaining cubes sorted into scattered single cubes, count the number of cubes. Written report the number of tens and then the number of ones, and signal the full number of cubes. The maximum total will be 40

Determine totals to twoscore past counting tens and ones using objects in ten-frames
Objects sorted into boxes of 10 and remaining objects sorted into scattered unmarried objects, count the number of cubes. Report the number of tens then the number of ones, and indicate the full number of objects. The maximum total will be 40

Determine totals by counting tens and ones using scattered and unlike objects in x-frames
Objects sorted into boxes of 10 and remaining objects sorted into scattered unmarried objects, count the number of cubes. Report the number of tens then the number of ones, and indicate the total number of objects

Decide the total of a set up of 'coins' using 10s, 5s, and 1s
In this activity, you will exist given coins of various values (10 cents, 5 cents, 1 cent). You will then count the corporeality of money you lot have in each problem

Correspond numbers to 40 using base-10 rods and cubes
Y'all will be given several rods of 10 base of operations 10 cubes along several unmarried base 10 cubes. You will then be asked to select a certain corporeality of cubes from the larger amount y'all beginning with. The maximum value you will take to count out will be 40

Place names of numbers to xl on a number line
A number line with present numbers will be given to you in this activity. You will then have to name numbers that follow the ones already on the numbers line. The maximum value of the highest number you will potentially have to proper noun is twoscore

Make up one's mind a missing number to twoscore on a number line and identify its written name
A number line with present numbers volition be given to yous. Yous volition have to fill up in blanks on the number line with the number that is missing. You will and so have to name these numbers. The maximum value of the highest number you demand to name is 40

Decompose 2-digit numbers to 40 into tens and ones with and without a model of base-ten blocks
You volition be given various 2 digit numbers. You lot will be asked to decompose each number into tens and ones or yous will be given the decomposition to start and have to identify the number that matches each decompostion

Decompose 2-digit numbers to 40 into a round ii-digit number plus ones
In this activity, you will be given coins of various values (x cents, 5 cents, 1 cent). You volition then count the amount of money you take in each problem

Solve equations that add or decrease 1 or 10 with and without modeling with base-10 blocks (Part 1)
You will add 1 to various ii digit numbers less than twoscore in this activity. You will use base ten number blocks to model each addition equation

Solve equations that add together or decrease 1 or 10 with and without modeling with base of operations-x blocks (Part two)
Y'all will add 10 to various two digit numbers less than twoscore in this activeness. Yous will use base 10 number blocks to model each addition equation

Solve equations that add or subtract i or 10 with and without modeling with base-10 blocks (Part 3)
You will subtract ane from various two digit numbers less than 40 in this activity. You volition use base of operations 10 number blocks to model each subtraction equation

Solve equations that add or subtract 1 or ten with and without modeling with base of operations-10 blocks (Part 4)
You will decrease ten to diverse two digit numbers less than forty in this activity. You will use base 10 number blocks to model each subtraction equation

Solve equations that add or subtract 1 or 10 with and without modeling with base-10 blocks (Part v)
You lot will add ten to, add together 1 to, subtract 1 from, and subtract ten from diverse ii digit numbers in this activity. You volition not be able to apply base ten number blocks to model each equation

Topic B: Comparison of Pairs of Two-Digit Numbers
Students compare and social club numbers, reinforcing their understanding of place value and sequence. They use familiar base-x blocks, number line, and begin using inequality signs.
Topic C: Improver and Subtraction of Tens
Students work with round numbers to reinforce place value understanding of 10 more and ten less. They use equations and the number line to solve addition issues and counting patterns.
Topic D: Add-on of Tens or Ones to a 2-Digit Number
Students rely on growing understanding of exchanging to model and solve two-digit add-on problems with exchanging using familiar models and new strategies.
Solve equations that add or subtract 1 or x with and without modeling with base-10 blocks
Yous volition add single digit numbers to various two digit numbers less than xl in this activity. Y'all will use base x number blocks to model each addition equation

Model and solve addition equations that add a unmarried-digit number to a ii-digit number using a number line
You will be calculation unmarried digit numbers to ii digit numbers in this activity. You will be allowed to use a number line to assist with these addition equations

Solve equations that add a single-digit number to a ii-digit number (Function 1)
You will be adding unmarried digit numbers to two digit numbers in this activity. All the same, you will not be allowed to use a number line or any other visual aids to help with these addition equations

Cull matching addition expression and sum
For this activity, you will be adding single digit numbers to two digit numbers. You volition be using a game board to guide your trouble solving. Once yous attain the other side of the game board, yous win

Decide a missing addend to add up to the next circular number with and without a model of base-10 blocks
For this activeness, you will exist deciding what number to add to the given two digit number to get to the next round number. Yous will be doing this with and without the assistance of a base 10 cube model

Decide a missing addend to add upwards to the next round number and solve the equation (Function ane)
For this activity, you will be deciding what number to add to the given two digit number to get to the next round number after placing the 2 digit number on a number line. You lot will be doing this with the use of a number line

Decide a missing addend to add up to the next round number and solve the equation (Part 2)
For this activity, you will be deciding what number to add to the given ii digit number to get to the next circular number. Yous will be doing this without the use of any visual aids

Determine a missing addend to add up to the next round number and solve the equation (Role 3)
Using a number line, yous will determine what to add together to the given two digit number to get to the next round number. You volition also need to effigy out what the showtime digit is of that round number

Model and solve two-digit addition equations with exchanging using base-x blocks
Using a base of operations 10 number cube model, yous volition solve add-on equations. You will decide how much of the second addend will exist needed to get the first addend to the side by side round number. You will then add the remaining corporeality to get the concluding sum

Solve addition equations across ten using a number line
Using a number line, you will solve addition equations. You will make up one's mind how much of the 2d addend will exist needed to get the first addend to the next circular number. You volition then add the remaining blocks to become the final sum

Solve addition equations across a ten past splitting an addend to make a x
Without the use of whatsoever visual aids, you will solve addition equations. You will decide how many of the second addend will be needed to go the start addend to the next round number. Y'all will then add the remaining blocks to get the terminal sum

Solve equations that add a single-digit number to a two-digit number (Function 2)
For this activity, y'all will be adding single digit numbers to 2-digit numbers. You lot will be using an interactive illustration to motivate y'all equally you complete these addition equations. The maximum value of the sums will be 40

Topic E: Addition of Tens and Ones to a Two-Digit Number
Students synthesize their learning from the previous topic to add tens and ones to a 2-digit number. They are supported by the familiar model of base-10 blocks and footstep-by-step guidance.
MODULE 5. Identifying, Composing, and Partitioning Shapes
Topic A: Attributes of Shapes
Students learn the bones attributes of shapes: lines, airtight figures, sides, and corners. They learn to identify triangles, rectangles, squares, trapezoids, and hexagons.
Identify the lines
Learn to identify lines. Select lines in various orientations from amidst a group containing lines and curves

Identify curved lines
Learn to place curves. Select curves in diverse orientations and forms from amid a group containing lines and curves

Identify airtight shapes
Identify open and closed figures. Select all of the open up or closed shapes as directed out of a fix that contains both

Identify shapes with a given number of sides
Select all figures with a given number of sides out of a set that contains a variety of closed figures

Count the number of sides and corners of shapes
Requite the attributes of a triangle, rectangle, and hexagon. Select whether it is an open or airtight shape and enter how many sides and angles it has

Identify hexagons
Learn the characteristics of a hexagon. And then, select those shapes that are hexagons

Place triangles, rectangles, squares, and hexagons
Sort triangles, rectangles, squares, and hexagons by clicking on the creature that eats each of those types of shapes

Identify a trapezoid
Learn to identify a trapezoid. Choose the trapezoid out of 2 quadrilaterals, then state the attributes of a trapezoid

Draw given shapes
Practice drawing different shapes as directed on a peg board

Identify given shapes
Choose the proper noun of the polygon out of 2 choices

Identify shapes of everyday objects
Given a motion picture of a real-world object, choose the correct name of the polygon out of 4 options

Topic B: Halves and Quarters of Rectangles and Circles
Students learn to identify and count equal parts in a partitioned shape. They larn the names for halves and quarters, and utilise these names in identifying shapes partitioned equally such.
Topic C: Application of Halves to Tell Fourth dimension
Students explore digital and analog clocks to understand the passage and identification of time. They larn parts of the clock and different types of fourth dimension note: X:Xx, X o'clock, X-30, and one-half past 10.
MODULE 6. Identify Value, Comparison, Addition and Subtraction to 100
Topic A: Numbers to 120
Students use familiar representations (objects, x-frames, base-10 blocks, number line, place value cards, number names, and equations) to extend their place value understanding to higher numbers within 100. They brainstorm building their mental model of the hundred chart by understanding the relationship between numbers in columns and rows. They reinforce the understanding that 2-digit numbers are equanimous of a round number (or tens) plus ones.
Determine a missing circular number to 100 on a number line and identify its written name
For this activeness, you will exist using a number line. Y'all will be naming numbers by tens starting at zero and catastrophe at 100

Position round numbers, in both digits and words, on a vertical number line
For this activity, you will be placing circular numbers between zero and 100 on a number line. The numbers will be written on zeppelins that you lot "land" on the number line

Determine 2-digit totals based on base-10 blocks and place value cards
Base 10 number cubes volition be used for this activity. Y'all volition be given a sure amount of 10 cube number rods and certain amount of individual numbers cubes to determine the total amount of number cubes

Decide 2-digit totals of objects in ten-frames or base-10 blocks
You will exist given groups of 10 objects arranged in x-frames forth with individual objects exterior of the x-frames. You lot will then use the 10-frames and individual objects to count the total number of objects

Determine totals by counting objects with or without filling ten-frames
Ten-frames volition be used to assist with determining the full amount of objects for this activity. You lot will end filling every bit many 10-frames as possible and add the remaining objects to the the pbjects arranged in 10-frames

Represent a given two-digit number with base of operations-10 blocks
For this activity, base 10 number cubes volition be used. You will utilise 10-cube rods and individual number cubes to represent the amount indicated in each problem

Identify 2-digit round numbers
For this activeness, you lot will be selecting circular numbers less than or equal to 100 for this activity. You lot will be given a grouping of numbers and volition have to pick the round numbers from each group

Decompose 2-digit numbers into a round number plus ones
A series of two-digit numbers less than 100 will be give to you to start this activeness. You will break downwards each number into a circular number and a single digit number

Determine 2-digit totals of base of operations-10 blocks by counting tens and ones
A base of operations 10 number cube model will exist used for this activity. You lot volition be given a certain corporeality of 10-cube rods and private number cubes. You volition and then determine how many cubes there are altogether

Determine totals by counting tens and ones using scattered and unlike objects in 10-frames
Groups of similar and unlike objects arranged in and exterior of ten-frames will be used for this activity. You will then count the full number of objects overall

Decompose ii-digit numbers into tens and ones with and without a model of base-10 blocks
Base ten number cubes will be used for this activity. With this number cube model, decompose two digit numbers. Each number will either be represented with number cubes at the get-go or you will accept to correspond each number with number cubes earlier the

Solve +/- ane and +/- ten equations with and without a model of base-ten blocks
Yous will add together 10 to, add 1 to, subtract 1 from, and subtract 10 from various two digit numbers in this action. Yous will non able to utilize base 10 number blocks to model each equation. The maximum value of each last full will be 99

Count forward and astern within a x on a number line
A number line will be used to assistance You with counting forrard and backward. Equally you count forward and backwards, you will fill in the given blanks on the number line provided

Align a scattered set up of numbered, non-sequential objects in ascending club
Given a visual aid, you volition be arranging numbers in ascending order. The numbers in this activeness volition be less than 100

Align a scattered set of numbered, non-sequential objects in descending lodge
Given a visual assistance, you volition exist arranging numbers in descending order. The numbers in this activity will be less than 100

Compare ii-digit totals with a set up of 10, 5, and 1 coins
Given a certain amount of coin in coins of 1 cent, 5 cents, and ten cents and a group of items with various prices, you will decide which item you can purchase with the corporeality of money you are given

Place missing numbers on a hundred chart
A by and large filled in nautical chart of numbers in guild from 1 to 100 will be given to you lot at the outset of this activity. You will then make full in the blanks with the missing numbers

Identify 10 less, 10 more, 1 less, and 1 more on a hundred chart with limited numbering
A slightly filled in chart of numbers in society from 1 to 100 will be given to you at the start of this activity. You lot volition then fill up in the blanks with the missing numbers

Calculation round numbers using blocks and bars
A model of base 10 number cubes will exist used for this activity. You volition be adding pairs of two-digit numbers. The maximum value of each sum will exist less than 100

Improver and subtraction of circular numbers
A model of base of operations 10 number cubes will be used for this activity. You volition be adding circular numbers in this activity. The maximum value of each sum volition be xc

Solve equations that add together two-digit numbers across a 10
Adding pairs of two digit numbers volition be the focus of this activity. Some problems involve the apply of turnaround facts. If you respond a question wrong, you will use base ten number cubes to help get the question right

Solve equations that add together or subtract a round number using a hundred chart
A hundred nautical chart will exist provided for this activity to consummate addition and subtraction bug. You lot will be calculation and subtracting round numbers from non-round two digit numbers

Place missing numbers in columns on a hundred chart with express numbering
A hundred nautical chart volition be given to you at the showtime of this activeness. You will need to fill in columns of this nautical chart by couting up by tens in each column

Identify ane more and 10 more on a hundred chart with limited numbering
You will exist given a hundred chart in this action. You will be calculation one or ten to each number indicated in the chart to get from one side of the chart to the other

Complete and solve equations that add or subtract a round number using a hundred chart
A hundred chart will be given to you in this action. You lot will use this chart to assist with adding round numbers to not circular numbers

Identify missing numbers on a hundred chart and decompose into tens and ones
A hundred nautical chart will be provided for you on this activity. You will identify what number should exist typed into the blank on the hundred chart. Then y'all will decompose the same number into tens and ones

Count frontwards across 100 and beyond 100 on a number line
You volition be given a number line with most of the values filled in. You will have to fill up in the blanks moving forward on the number line using the numbers provided on the number line already. You volition be providing values that are over 100 at times

Count backward beyond 100 and beyond 100 on a number line
You will exist given a number line with almost of the values filled in. Y'all will accept to fill in the blanks moving backwards on the number line using the numbers provided on the number line already. Yous will be providing values that are over 100 at times

Identify a missing three-digit number on a number line and its written name
A number line volition be provided for this activeness with most of the values already labeled. For each question, y'all will be filling in the 1 missing value. And then, you lot will be naming the number in words

Determine totals of objects in ten-frames across 100
You volition exist given objects pre-sorted into 10-frame boxes and some objects that are set off to the side on their own. You will have to decide how many objects are in the boxes and how many are off to the side to determine the total number of objects

Count base-ten rods beyond 100
Base 10 number cubes grouped into rods that are x cubes long will be made available at the beginning of this activity. You will and so have to determine how many cubes at that place are overall. The respond each fourth dimension volition exist a circular number

Make up one's mind totals beyond 100 using a base-10 flat, rods, and cubes
Base of operations ten number cubes grouped into 10 cubes rods along with individual cubes will be given to y'all at the outset of this activeness. Employ both of these visual aids to summate how many cubes in that location are overall. Some answers to the questions will be over 100

Topic B: Addition to 100 Using Place Value Agreement
Students utilise familiar base-x blocks, number line, and equations to work with round numbers. They rely on counting, place value, and improver/subtraction skills to solve problems. Students utilise familiar manipulatives to solve two-digit add-on problems with and without exchanging. They also solve ii-digit subtraction problems without exchanging.
Topic C: Coins and Their Values
Students explore the heads and tails sides of the penny, nickel, dime, and quarter. They learn the value of each money, how to count a collection of them, and how to count a mixed collection of coins. Students match coin image, proper noun, and value.
Place a penny and its value
Explore the appearance of both sides of a penny. Sympathise its value as one cent and calculate the total value of up to 6 pennies

Identify a dime and its value
Explore the advent of both sides of a dime. Understand its value as x cents and summate the total value of up to 6 dimes

Match a penny or dime to its name, appearance, and value
Select a coin name, paradigm, and value that all represent a dime or a penny

Place the total value of a collection of dimes and pennies
Given a selection of dimes and pennies, blazon the total value

Exchange between one dime and ten pennies
Count and exchange pennies for a dime. Use pennies and dimes to prove a full of 12 cents in 2 unlike ways

Identify a nickel and its value
Explore the appearance of both sides of a nickel. Understand its value every bit five cents and calculate the total value of up to 6 nickels

Lucifer a penny, nickel, or dime to its proper name, advent, and value
Identify whether a coin name matches the image shown. Match a penny, dime, and nickel with its name and value

Match a penny, nickel, or dime to its name, advent, and value (Part 2)
Place whether a coin shown matches the proper name given. Match a penny, dime, and nickel with its name and value

Identify a penny, nickel, or dime based on colour or size
Place pennies, nickels, and dimes from a collection of coins, even when the details of the coins are blurred

Exchange betwixt pennies, nickels, and dimes
Count and commutation between pennies, nickels, and dimes. Count the total of a collection of nickels and pennies

Bear witness a given total using nickels and pennies
Given a full value, choose nickels and pennies to equal the total

Identify a quarter and its value
Explore the appearance of both sides of a quarter. Empathize its value every bit twenty-five cents. Sort pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters based on value

Source: https://happynumbers.com/math/grade1
Posted by: inmansuce1958.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Many Different Sums Of Money Can Be Made From A Penny A Nickel A Dime And A Quarter"
Post a Comment